Do you recognize these images?
One of the very first CAPTCHAs, just doing math! The challenge is written in an image.
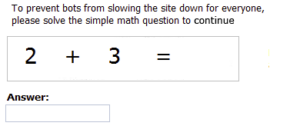
The text was distorted, so distorted that sometimes it couldn’t even be read.
Next up is the traffic light challenge. There are multiple versions with different objects: cars, bicycles, etc., but all of them always relate to the road and road signs!

The famous challenge we have to solve before accessing a resource we would like to consult is called CAPTCHA , which stands for “ Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart ”. It was first developed in 2000 by Luis von Ahn, Manuel Blum, Nicholas Hopper and John Langford at Carnegie Mellon University. This technology was created to prevent automated bots from abusing online services.
And you know what, their time is running out !
What’s wrong with CAPTCHA?
CAPTCHAs, designed to protect websites from bots, have become increasingly complex, frustrating human users. Paradoxically, bots (in the web sense, i.e., automated scripts that crawl entire websites), thanks to advances in AI, can now solve these puzzles in milliseconds.
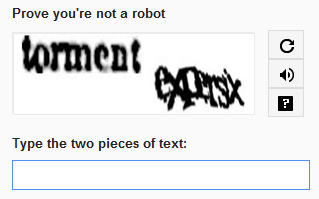
Traditional CAPTCHAs, such as garbled text recognition, are easily circumvented by modern AI systems. Alternatives, such as sliding puzzles or biometrics, also pose challenges in terms of privacy and accessibility. They once asked a simple question like “copy the text,” but have now evolved to require users to solve complex questions. A task as simple as logging into a social media account or trying to pay utility bills has become a headache.
CAPTCHAs have evolved over the years to adapt to growing online threats and ensure website integrity. Developers are looking for solutions to distinguish good bots from bad bots, but the task is becoming increasingly complex as AI advances.
Indeed, after solving a CAPTCHA, the data from our efforts to label these blurry grids of traffic lights, text, or buses is used to train machines, which then improve by bypassing CAPTCHAs and convincing the systems that they are human. Moreover, all these challenges presenting a grid of elements to choose from are always based on illustrations of situations taken on public roads. In fact, this type of challenge designed by Google is also used to train its AI, which they use in their self-driving cars! Now you understand why you should always recognize cars or motorcycles, and never cats or dogs.
Today’s AI systems can solve CAPTCHA challenges. They can “read” distorted text, so the squiggly or compressed letters of the original CAPTCHA tests are easy for them to read. Using natural language processing and machine learning, AI can decode even the most confusing words.
These days, many bots are capable of attacking social media platforms, e-commerce sites, and online forums. Fake accounts spread misinformation, post spam, or purchase limited-quantity items during sales. In many cases, CAPTCHAs are no longer able to stop this abuse.
And then?
CAPTCHA developers have therefore been forced to make them more complex to make them impervious to AI. That said, even CAPTCHA developers no longer really believe in the future of this technology. New verification methods are constantly being introduced. Some systems, including Google’s ReCaptcha v3 (introduced in 2018), no longer ask you to solve puzzles. Instead, they observe how you interact with a website. This new version of the famous reCAPTCHA becomes transparent to users; it’s just a script analyzing your journey on the site, without interrupting you to pose a new challenge.
The reCAPTCHA v2 version, which requires the user to simply check a box, is still widely used. Similar implementations exist where you no longer even need to click or press a button.

No challenge, just click, wait 1-3 seconds, and there you go!
Web companies will therefore have to begin distinguishing between these good bots and these bad bots. This area still requires a lot of attention, but digital authentication certificates are proposed as a possible solution.
Today, with the introduction of reCAPTCHA v3, Google no longer even requires users to interact with you. Based on cookies and JavaScript, the system assesses the likelihood that the user is human or a robot.
You know it’s there when you see this image, usually in the lower right corner of a web page:

In summary
The CAPTCHA is no longer the simple and reliable tool it once was; it is proving increasingly ineffective at distinguishing humans from robots. AI has made it obsolete and it has even become boring. It now needs to be reinvented. Probably the CAPTCHA of the future, to protect your site from bad AI, will be built on good AI… knowing that good and bad AI could be the same tool used by different people, with different objectives!
According to Oui, je suis humain: la détection des robots ne fonctionne plus

